This article aims to delve into the basics of STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning) and explain why all three phases are central to the implementation of performance marketing.
Content
Preparing for Performance Marketing with STP
Integrating STP into Performance Marketing Campaigns
Challenges and Possible Solutions in STP Implementation
Introduction
Performance marketing is one of the essential elements for both growth and overall success of companies. This is because it focuses on the execution of specific actions, such as making a sale or acquiring a certain number of potential customers. At the heart of this preparation is the well-known strategic trinity of Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning ( STP) - a framework that guides marketers to identify their most valuable customers, target them effectively and position their offerings to have the greatest impact.
This article aims to delve into the basics of STP and explain why all three of these phases are central to performance marketing. We will also focus on how this strategy can be used to create campaigns that not only achieve their goals, but even surpass them.
In short, by understanding and implementing the STP model, you can ensure that your marketing activities are not 'just' visible or audible, but also have a positive impact on your bottom line, easing your path to sustained growth and competitive advantage.
Preparing for Performance Marketing with STP
Once you decide to apply performance marketing, it's a good idea to use the STP (segmentation, targeting and positioning) model to lay the groundwork for effective campaigns. This preparation is not just about understanding the market, but also about strategically aligning your marketing activities to ensure the best possible engagement and conversion rates. In this section, you'll learn how to use the STP approach to build a solid foundation for performance marketing:
.png?width=602&height=301&name=Kopie%20n%C3%A1vrhu%20Segmentace%20(2).png)
Preparing for Segmentation
The segmentation phase involves breaking the market into easily manageable, homogeneous groups based on common characteristics. This careful process involves the following activities:
- Research and Data Collection: Start by collecting comprehensive market data. This may include demographic data, buying behaviour or psychographic profiles. Use tools such as customer surveys, social media analysis or market research reports to build a content-rich data set.
- Define Criteria: Define clear criteria for audience segmentation, which can include, for example, a wider range of demographic factors (location, age, gender...) but also more precise psychographic and behavioural indicators (purchase behaviour, customer journey, engagement...). The goal is to identify segments that are numerous, accessible and that respond to your marketing activities.
- Identification of Segments: Once the criteria have been established, identify the different market segments. Each segment should represent a unique subset of the market with specific needs and preferences.
.png?width=602&height=301&name=Kopie%20n%C3%A1vrhu%20Segmentace%20(1).png)
Targeting Strategy
After identifying the segments, you need to select the most valuable segment(s) to target with your marketing resources. This selection should be based on:
- Growth Potential: Evaluate which segments show promising growth trends and willingness to engage with your brand.
- Profitability Analysis: Assess the potential profitability of each segment based on factors such as purchasing power and loyalty.
- Cost of Acquisition: Take into account the cost of reaching each segment. Lower acquisition costs usually mean higher profitability potential.
Determining the Positioning
The final step, positioning, involves creating a compelling value proposition that will resonate with the target segment. In this phase, you differentiate your brand and offer in the following ways:
- Creating a Value Proposition: Articulate a clear and compelling reason why your target segment should choose your brand over the competition.
- Content Strategy: Develop messaging and content that directly addresses the identified needs and wants of your target segment and reinforces your unique brand position.
- Continuous Optimization: Use feedback and performance data to refine your strategy to ensure it remains consistently relevant and compelling to your target audience.
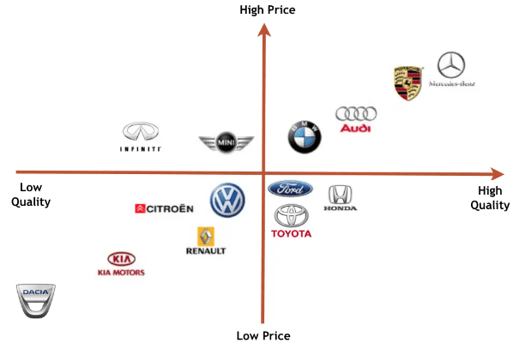
The picture is only for illustration
As you can see, each brand has its own particular position. Some brands are known for offering a very high quality product, but at a high price. Others, on the other hand, try to fight the competition by setting a low price, but this takes a toll on quality. It follows that you should also create a similar chart and define where you would like to be, where you actually are, and at the same time where your competitors are.
Integrating STP into Performance Marketing Campaigns
How to integrate STP strategy into performance marketing campaigns?
- Tailored creatives and messaging: Use insights gained from segmentation and targeting to develop messaging and creatives that are directly relevant to the interests, needs and preferences of selected audience segments. Customized content increases relevance and engagement, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Channel selection: Use your knowledge of your target segments to determine the most effective channels to reach them. Whether it's social media platforms, email marketing, search engines or display advertising, choose the channels where your audience is most active and receptive.
- High quality positioning: Positioning your product or service to highlight its unique value is key. Use the data from your positioning strategy to highlight the benefits and features that are most important to your target audience and differentiate your offering from your competitors in the marketplace.
- Monitor and optimise performance: If STP is the foundation of your campaigns, you can constantly monitor performance metrics and gather feedback from your audience. This data-driven approach enables ongoing optimization to ensure your campaigns remain effective and efficient in reaching your target segments.
Challenges and Possible Solutions in STP Implementation
In this section, we look at common challenges and their practical solutions for all three steps of the STP model:
Potential Challenges in Segmentation
Challenge: Data Overwhelm
Due to the vast amount of data available, identifying relevant data for segmentation can be quite a complex task.
- Solution:
Focus on key data points that align with your business objectives. Use data analysis tools (Google Analytics, HubSpot, Mixpanel, Hotjar...) that can filter and sort data based on predefined criteria, making it easy to manage and interpret.
Challenge: Identifying the most valuable segments
Not all segments are equally profitable or generally suitable for targeting.
- Solution:
Conduct a thorough analysis of each segment's potential ROI. Consider factors such as size, growth potential, alignment with your brand values and product portfolio offering.
Potential Targeting Challenges
Challenge: Overlapping Segments
Overlapping segments can lead to confusion in targeting and messaging.
- Solution:
Clearly define each segment with specific characteristics to minimize overlap. Use targeted messages that resonate with the unique aspects of each segment.
Challenge: Adapting to Dynamic Market Conditions
Rapid changes in market conditions can cause previously defined segments and objectives to become irrelevant.
- Solution:
Regularly review and update your segments and target markets based on the latest market research and consumer trends. Stay flexible and be prepared to change your strategy as needed.
Potential Positioning Challenges
Challenge: Differentiating Yourself from the Competition
Standing out among a large number of competitors can be very difficult.
- Solution:
Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP) and make sure it is clearly communicated through all marketing channels. Understand what is really important to your target audience and tailor your positioning to highlight these aspects.
Challenge: Maintaining Consistent Positioning Across Channels
It seems obvious, but in practice it is very often the case that the positioning of the same company across channels varies significantly.
- Solution:
Develop a comprehensive positioning statement to guide all marketing communications. Ensure that all marketing teams are aligned and understand the underlying positioning strategy.
More Tips for Overcoming Challenges with the STP Model
- Leverage technology: Use CRM systems, analytics tools and marketing automation platforms to gather information, manage data and automate targeted campaigns.
- Continuous learning: Stay abreast of industry trends, changes in consumer behaviour and technological advances that may impact your STP strategy.
- Customer feedback: Regularly get feedback from your target audience to understand their changing needs and perceptions, allowing you to adjust your strategy accordingly.
Conclusion
The STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning) model is an effective framework that, when skillfully incorporated into performance marketing strategies, can significantly increase the efficiency and effectiveness of your campaigns. By carefully segmenting your market, accurately targeting the most prospective segments and positioning your offer to directly appeal to your chosen target audience, you'll lay the foundation for marketing campaigns that will resonate strongly with your audience.
This strategic alignment will ensure that every marketing spend is spent wisely, leading to higher conversion rates, fostering brand loyalty and ultimately contributing to the overall success of your business. Once you're ready to start leveraging performance marketing, use the STP model as a guide to create campaigns that not only reach, but also truly engage your target audience, making your brand stand out in today's crowded marketplace.
However, if you're not sure how to implement or even create the STP model, feel free to contact us to arrange a free consultation. Our performance marketing specialists will be happy to help you with this daunting task.
FAQ
1. What is STP?
STP stands for Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning - a strategic approach in marketing that aims to identify and reach specific audiences with tailored messages.
2. Why is segmentation important?
Segmentation helps marketers divide a broad market into smaller groups with similar needs or characteristics.
3. How does targeting work within STP?
Targeting involves selecting which market segments to target based on their potential value to the firm, such as profitability, size, and availability.
4. What is positioning?
Positioning is the way in which a product or brand is perceived in the minds of the target group, and differentiates it from competitors by emphasizing unique benefits or features.
5. Can STP be used in digital marketing?
Yes, STP is highly effective in digital marketing because it enables personalized advertising and content strategies that appeal to specific audience segments.
6. How to select the right target segment?
Consider factors such as market size, growth potential, profitability, and how well you can meet the needs of that segment compared to your competitors.
7. Is the STP only for large companies?
No, companies of all sizes can benefit from using the STP model to reach and engage with their target customers more effectively.
8. How often should I review my STP strategy?
Regularly review and adjust your STP strategy to respond to market changes, customer feedback and competitive dynamics, at least annually or as needed.